|
|
|
Introduction
What is TBIC ?
Total body irradiation couch (TBIC) aims to deliver a uniform dose to the body while limiting the dose to lung and kidney. Several techniques have been reported for approaching this goal. One of the techniques uses a computer controlled translating couch combined with transmission blocks for lungs and kidneys. Although the technique enhances patient comfort and consistency, dose non-uniformity exists due to varying patient thicknesses, and shielding of critical structures is compromised by the large partial shadow produced by beam divergence. The technique is couch translations to modulate the intensity of the beam during the treatment by modulates the velocity of the couch (Fig.1) [1].
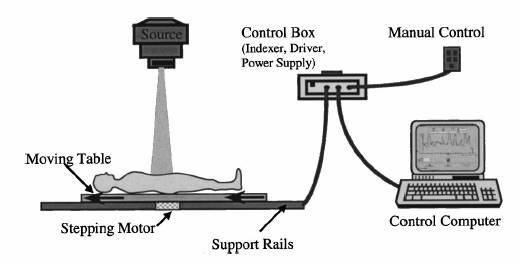
Fig.1: Translational couch system scheme
Background
Total body irradiation (TBI) with photon beams is administered in radiation therapy centers for variety of the clinical situations with different techniques. The radiation dose delivered throughout the patient body varies mainly due to the variation in patient thickness. However, it is desired to keep the dose non-uniformity within 10% of the prescription dose for best clinical results. Partial shielding for specific organs (e.g., lungs and kidneys) is often provided to minimize normal tissue complications [1].
1- The most common irradiation technique consists of anterior-posterior fixed beams with the patient in standing position. This technique requires a source to surface distance (SSD, Fig.2) in excess of 3 m to encompass the patient within the large beams. The sickness and fatigue associated with chemotherapy makes it difficult for many patients to hold a standing position during the prolonged radiation time, resulting in poor reproducibility in setup (Fig.3) [5].
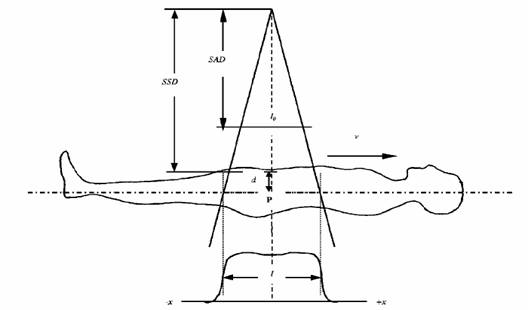
Fig. 2: distances from source to patient


Fig.3: The TBI Stand facilitates treatments of patients in a standing
2- To alleviate patient discomfort to some extent and to overcome the limitation of treatment room dimensions, patients are treated in a semi seated position with bilateral beams. However, this technique suffers from poor dose uniformity and does not allow for effective shielding of the lungs and kidneys (Fig.4) [7].
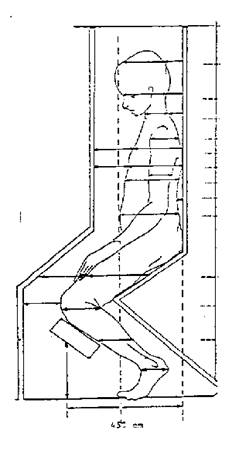

Fig.4: Semi seated position
3- A few centers have employed a sweeping arc beam with patients lying on the floor under the machine. However, this technique requires utilization of a sophisticated custom-made compensator for each patient [6].
4- A translational couch technique (Fig.5) is utilized in which patient rests on a couch in supine position and is transported horizontally through a vertical beam. This technique presents a special challenge regarding dosimetry due to the moving beam dose delivery [1].
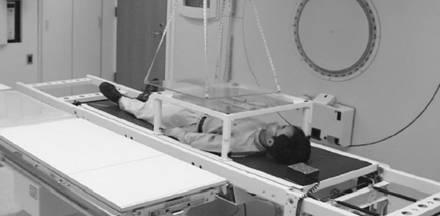
Fig.5: Translational couch
CANADIAN ORGANIZATION OF MEDICAL PHYSICISTS have developed a variable speed translating patient couch system for the delivery of Total Body Irradiation (TBI). For a whole body Rando-like phantom, dose variation at mid-plane relative to the prescription point (navel) can be as high as 15 % (neck or legs) with a constant velocity. By taking into account variations in body thickness the intensity modulation produced from variable velocities effectively result in a uniform dose distribution at mid plane. The couch control user interface and dose planning optimization procedure for determining velocity distribution are described [1].
COUCH CONTROL
A moving-couch TBI system has been designed and constructed (Fig. 6). It consists of a couch driven by computer via a control box. An in-house software (CONTROL TBI) uses the velocity distribution previously computed at planning time to control treatment delivery. In addition, the graphical user interface provides real time display of treatment evolution. Also, the velocity and the position of the couch are reported independently by another system. Our remote-controlled translation system can drive and vary the couch at any velocity within the useful clinical range of 1 to 30 cm/min. Speed is controlled with an accuracy better than 0.5% [1].

Fig.6: Couch control schematic
BEAM WEIGHT OPTIMIZATION AND VELOCITY DISTRIBUTION
To perform the planning dosimetry, a large number of beams (up to 72) are distributed over the entire body length. A macro was written to interact with the treatment planning (TheraplanPlus from Theratronics) to automatically generate the beams and extract their contribution on each CT slice. The distance between beams is calculated using field length, patient length and the number of beams. Beam weights are varied with an optimization routine in order to minimize dose variation at mid plane of the patient, taking into account the patient anatomy (CT Scan). The treatment planning system performs the final dose calculation with the proper beam weights. Each beam weight can then be converted into velocity using the reference value .Velocity changes occur between two beams [1].
What is our solution?
Our solution is Translational Couch Technique with some important modifications; the need for modifications comes from the conditions and the problems that we faced it in our case like dimensions and prices of the known products of TBI available in the market.
Why did we chose this chouse and make modifications?
There are some reasons:
1- TBI translational couch is the best technique according to the dose uniformity, patient comfort and suitable with different accelerator machine.
2- Low cost of the parts that needed for the system and the working of the parts utilized ordinary workshops.
3- Our abilities (financial, engineering skills and time frame) are suitable for this technique.
What did we add?
The important things that we added in our new design are:
1- We made the bed of the couch (Structure of the system including the guider) of tow units to facilitate entering of the system in the small rooms and corridors in the university hospital.
2- We decreased the price making local designing and manufacturing.
3- We utilized power screw instead of the belt and stepper motor.
The different benefits of our project are:
1- Positive effect on the national economy because this will motivate the technology independence and local manufacturing.
2- We produced solution for the patients to help them.
3- We motivate the different foundations and companies to support our collage and the other engineering and science collages by give them opportunity to solve the problems and push the national industrial forward.